Singer Ali Aftab Saeed (best kn0wn for “aloo anday“) has started commenting on the news. The first two episodes are pretty funny. Check it out..
Category: Culture
Mass Psychology in the Age of Trump
Trump is not the first-ever Republican President with right-wing followers. However, he and his Presidency elicit a visceral response from liberals, both in the United States and abroad. This article in Democracy Journal takes a detailed look at why this happened.
Excerpts:
“What precisely is it about Trump that drives liberals to these cataclysmic views? The answer has to do as much with liberals as with Trump himself. First, there is the nature of liberal ideology itself, which—because of its peculiar characteristics and internal contradictions—contributes to the present situation. Second, there are psychological factors, the dispositional tendencies of those who are drawn to liberal ideology. These two elements are related because there is a close and reciprocal connection—what Max Weber called an “elective affinity”—between psychological needs on one hand and the philosophical contents of an ideology on the other.”
“A mad social scientist could not have devised a character who is more antithetical to the liberal worldview than Donald Trump—even a staunch conservative with a more disciplined commitment to right-wing ideals. Trump is unique in his ability to provoke, upset, and irritate those with liberal sensibilities. No doubt this is part of his appeal to a certain segment of the population—the ones who have been told since Nixon that “liberal elites” were laughing at them.”
We are now equipped to answer the question: Why does Trump—even more than other conservatives—make liberal brains go haywire? It is because he makes it impossible, in practice, for liberals to be tolerant (egalitarian), rational, and optimistic about human nature—three things that are essential aspects of liberal ideology and liberal psychology. Trump makes it preposterous, in other words, for liberals to be “liberal” in the usual sense.
Like a spoiled, spiteful, indifferent king, he makes no pretense of listening to or representing us—half the nation—in any way. In this respect, he is worse—more personally contemptuous of liberal norms, traditions, and accomplishments—than Nixon, Reagan, and Bush. If Trump were more religious he would resemble a pre-Enlightenment figure; it would be difficult to find a less scientifically informed member of the upper class. And yet the whole country, it seems, is held hostage to his narcissistic wounds, authoritarian rants, and Twitterstorms.
“In a preface to The Mass Psychology of Fascism, Wilhelm Reich wrote that “‘fascism’ is only the organized political expression of the structure of the average man’s character.” The fact that authoritarian inclinations are so mundane and quotidian means that they are a constant danger—and a constant source of anxiety for the liberal. It would be foolish at this historical moment to suggest that fascism has come to America. It has not. But to many of us, it feels as if we are closer to it than we ever thought possible.”
Matrix Movie Review
The Wachowski siblings said they created the Matrix inspired by the Ramayana, Bhagavad Gita and Buddhism. The Matrix is a great summary of Arya culture, values, philosophy, science and civilization. Veedu Vidz is one of the wisest commentators with Hindustani Bharatiya heritage.
Debt Cancellation, the Bible and Jesus
An interesting article, very pertinent for the current economic mess in the world. Maybe Zachary can weigh in.
Excerpts
Michael about his Forthcoming book Forgive Them Their Debts: Credit and Redemption that comes with an astounding re-reading of the Bible and the true meaning of the life and persecution of Jesus. Based on scholarly breakthroughs in decoding ancient languages, it places a debt cancellation message inherited from Babylonian times at the center of Mosaic law and the Jewish Bible. And when it comes to Jesus, his message is revealed to be a social justice message. Through the lens of this reinterpretation, Jesus was actually an activist advocating for debt cancellation. He died not for the sins of the people but for their debts.
In Sumer, and Babylonia, around 2500 B.C., and every new ruler, when they would take the throne, would start his reign by canceling the debts. In Sumer, the word for that was amargi, in Babylonian the word during Hammurabi’s dynasty was andurarum.
Hebrew deror, is a cognate to Babylonian andurarum, and the Jubilee year was word-for-word exactly the same debt cancellation and freeing of the bond servants and restoration of land that you had occured for 1,000 years in the Near East, and was still occurring in the first millennium BC.
What I realized is that when Luke 4 reports the first speech of Jesus, when he goes to the temple and gives a speech, his first sermon, he unrolls the Scroll of Isaiah, and said he has come to essentially proclaim the Jubilee year …. The word he used, and that Isaiah used, the deror, was this Babylonian, Near Eastern long tradition that was common throughout the whole Near East.
Business debts were not forgiven. The debts that were forgiven were personal debts, agrarian debts, and the idea was to liberate the bond servants so that they could be available to perform the corvée labor, which was the main kind of taxation in the Bronze Age, and serve in the army. If you were a debtor and you were a bond servant to a creditor, you wouldn’t be available for corvée labor, you’d be working (for) the creditor, you wouldn’t be available for the army.
The Romans were the first society not to cancel the debts, and there was civil war over that. A century of civil war from 133 BC, when the Gracchi Brothers were killed by supporting the population, to 29 BC when Augustus was crowned. There was a civil war where the advocates of debt cancellation were put to death. Just as Cleomenes in Sparta, in the late third century, was put to death, and Agis, his predecessor earlier in the third century BC, were put to death for advocating debt cancellation. So there was three centuries of constant civil war over this, and ultimately the creditors won, largely by political assassination of the advocates of debt cancellation, who almost all came from the upper class. They were upper class reformers, they were not lower-class particularly. They were the scholars, just as Jesus was a rabbi.
Most debts did not occur from lending money. It’s easier today to figure if you have a debt, you must have borrowed it. But three quarters of the debts in Babylonia, for instance, where we have records because they were on clay, cuneiform records that were baked and have survived, most debts were simply unpaid bills. The debts were unpaid taxes, unpaid debts, unpaid rent, and unpaid obligation for services that had been supplied.
And so Judaism took the debt cancellation out of the hand of kings, where it had been in the Near East, and put in the very center of their religion. In Leviticus 25, again and again the prophets would say, “We’ve freed you from bondage, and if you’re going to maintain Judaism, you have to respect the debt cancellation.” And the Biblical prophets warned, if you don’t cancel the debts, you’re gonna be canceled. By Assyria, by Babylonia. And they blamed the capture and destruction of Judea and Israel on the fact that they had veered away from the law of God and did not cancel the debts.
Tribes: When does the concept of a general debt cancellation disappear historically?
Michael: I guess in about the second or third century AD, that was downplayed in the Bible. And you had, after Jesus died, you had first of all St Paul taking over, and basically Christianity was created by one of the most evil men in history, the anti-Semite Cyril of Alexandria. Who decided to gain power by murdering his rivals, the Nestorians, by convening a congress of bishops and killing all of his enemies. Cyril was really the Stalin figure of Christianity, killing everybody who was an enemy, organizing pogroms against the Jews in Alexandria where he ruled.
And it was Cyril that really introduced into Christianity the whole idea of the Trinity. That’s what the whole fight was about in the third and fourth centuries AD. Was Jesus a human, was he a god? And essentially you had the Isis-Osiris, ISIS figure from Egypt, put into Christianity … The Christians were still trying to drive the Jews out of Christianity. And Cyril knew the one thing the Jewish population were not going to accept would be the Isis figure and the Mariolatry that the church became. And as soon as the Christian church became the establishment rulership church, the last thing it wanted in the West was debt cancellation.
Tribes: Has any modern society declared a Jubilee without a revolt of the creditor class?
Michael: Yes. There was a wonderful debt cancellation, the major debt cancellation of the modern era was in 1947 and 48, the German monetary reform, called the German economic miracle. The Allies canceled all German debts, except for debts owed by employers to their employees for the previous month, and except for minimum bank balances. It was easy for the Allies to cancel the debts, because in Germany most of the debts were owed to people who had been Nazis, and you were canceling the debts owed to the Nazis, the Nazis were the creditors at that time. And that freeing Germany from debt was the root of its economic miracle. So that is the prime example of a debt cancellation in modern times that worked.
More at https://www.nakedcapitalism.com/2018/04/michael-hudson-bronze-age-redux.html
Bi Kidude, Sri Lankan Baila and Traditional Drums
Recently saw a music video by Bi Kidude (Little Granny) from Zanzibar. I was struck by the similarities to Sri Lankan Kaffiringha or Manja music and old traditional music as in Panama Vannam and Yak (as in Yakkha) Thovil. (Panama is pronounced Paanaama, its a small village on the SE coast at the edges of the jungle).
Bi Kidude (Little Granny)
Fatma Baraka Khamis was Taarab singer from Zanzibar who was born around 1910. Bi Kidude won several awards including a WOMEX
 Award for her role in the culture of the Zanzibar Island. The iconic artist sadly passed away on April 17th, 2013. She very well might have been a century old. (see more here and video documentary“As old as my tongue – The Myth and Life of Bi Kidude” by director Andy Jones). In Bi Kidude’s words, I smoke, drink and sing. Not bad for a life to a hundred years.
Award for her role in the culture of the Zanzibar Island. The iconic artist sadly passed away on April 17th, 2013. She very well might have been a century old. (see more here and video documentary“As old as my tongue – The Myth and Life of Bi Kidude” by director Andy Jones). In Bi Kidude’s words, I smoke, drink and sing. Not bad for a life to a hundred years.
So here is one music video by Bi Kidude. A few other links, Dancing, Traditional Drums, and her Voice range (Alminadura).
Manja Music of Sri Lanka
Its the music of the Kaffirs (not a derogatory word in Sri Lanka). They were brought mainly by the Portuguese from Angola and Mozambique. The Tabbowa/Sirambiadi community in the west coast is a mix of African descendants and Sinhalese. Their music is now very much part of the Sri Lankan tradition. Below the group Ceylon African Manja performing in their village. This is youtube clip of the same group in a more formal setting.
Portuguese Burgers (Creoles) of Batticoloa (East Coast)
The Portuguese Burgers too sing and dance Kaffiringha music. Its is unknown if they have African roots.
Sri Lankan Traditional Music
A gravel voice and rhythms (as against melody) define traditional music. Immediate below women playing the rabane, a instrument played by women at village events, specially Sinhalese New Year. This particular video is from a five star hotel !!.
Second below the traditional Gajaba Wannama (dance of the King’s Tuske) with a modern dance ensemble. More Wannamas here.
Unheard of a couple of decades back, upper middle class girls/women playing the drums, or for that matter a traditional instruments. Now we have and all girl/women traditional drumming (watch it is good, their website http://www.thuryaa.lk/). The times are a changing.
note: Traditionally (at least the last century) dance for festivals, processions (perahera, eg. the Kandy Perahera) was done almost exclusively by men. One rarely saw women dancing, unless it was associated with Hindu Kavadi also part of the Perahera procession
Also see
http://sbarrkum.blogspot.com/2013/03/music-papare-video-angola-or-brasil.html
http://sbarrkum.blogspot.com/2011/01/galle-heliwela-exorcism-and-yak-natum.html
Thanks Mohamed Rizwan for linking the Bi Kidude video, Anton James for identifying Bi Kidude.
Ancient Egyptian, Arya and Greek history part 2
This article is a continuation of previous articles on ancient history from Zachary, Razib, Omar and myself:
-
Asians & Aryans
-
Jaydeepsinh Rathod on the historocity of Sanskriti
-
Ancient Egyptian, Arya and Greek history
-
Not all Aryans are Indian, though most Indians are part Aryan, and most Aryan ancestry is in India
-
Where do humans come from?
-
Ancient Arya Culture
Continue reading Ancient Egyptian, Arya and Greek history part 2
Why do Indians care about OIT/AIT
From my blog:
Razib: I follow your super feed and read your postings here and on Brown Pundits. The subject of the ancestry of South Asians comes up frequently. It seems to have a political valence that I, as an outsider, do not understand.
Can you explain it? or point us to an explanation?
My response is “British colonialism and modern-day culture wars.” I could say more, but honestly, I don’t care that much. The science is more interesting to me, and it’s a lot to keep track of. Can readers comment?
(Related: there are some Pakistanis who try and pretend as if they are descended from Persians, Turks, or even Arabs. The explanation is pretty straightforwardly summarized as “self-hatred”, though we could all elaborate on that).
Race Stereotypes in Medieval Islam (and some lines on cousin marriage)
This is just a short note from Irfan Muzammil. I hope to have Irfan writing blog posts directly on Brownpundits, but he is a busy man (and a real scholar), so this may take a while. Until then, I will be copying and pasting some of his musings..
Omar
Medieval Muslim scholars and courts seem to have been obsessed with the question of superiority of races: Arabs, Persians, Greeks, Indians, Franks, etc. (a debate that still rages). Abū Ḥayyān al-Tawḥīdi’s al-Imtāʿ wal-muʾānasah (Enjoyment and Geniality), a classic of Arab literature, presents discussions conducted in Baghdad at the court of the vizier Ibn Saʿdān al-ʿĀriḍ, who was executed in 984 AD after a short period in office. It illustrates the debates regarding a movement called Shuʿūbiyyah, which claimed cultural equality or superiority for the Persians over the Arabs. But the most surprising part, at least for me, is at the end.
First he quotes Ibn al-Muqaffa’, a prominent 8th century Persian philosopher, and seemingly a massive racist:
We said, ‘The Byzantines!’
“But he replied, ‘Not them either. They have strong bodies, they are good at building and at geometry but know nothing besides these two things and are good at nothing else.’
“we said, ‘The Chinese then!’
“He said, ‘They are good at handicraft and making artefacts; they have no deep thought or reflection.’
“we said, ‘well then, the Turks!’
“He said, ‘They are wild animals that can be made to fight.’
“we said, ‘The Indians?’
“He said, ‘People of delusion, humbug, and conjurer’s tricks.’
“we said, ‘The Africans!’
“He said, ‘Dumb beasts to be left alone.’
“Then we left the matter to him, and he said, ‘The Arabs!’ Continue reading Race Stereotypes in Medieval Islam (and some lines on cousin marriage)
South Asians and “communalism”
 In Who We Are and How We Got Here one of the things that David Reich states is that while China consists to a great extent of one large ethnic-genetic group, India (South Asia) is a collection of many ethnic-genetic groups. To some extent, this is not entirely surprising. People from the far south of the subcontinent look very different from people from Kashmir or Punjab.
In Who We Are and How We Got Here one of the things that David Reich states is that while China consists to a great extent of one large ethnic-genetic group, India (South Asia) is a collection of many ethnic-genetic groups. To some extent, this is not entirely surprising. People from the far south of the subcontinent look very different from people from Kashmir or Punjab.
But that’s really not what Reich is talking about. People in Hebei look quite different from people in Guandong. Perhaps less different than a Tamil from a Kashmiri, but still quite different. But these regional differences grade into each other along a cline.
South Asia is different because strong genetic structure persists within regions. Both Tamil and Bengali Brahmins share some distinctive genes with local populations, but genetically they’re still a bit closer on the whole to Brahmins from Uttar Pradesh (I say this because I’ve looked at a fair number of genotypes of these groups). Similarly, Chamars from Uttar Pradesh and Dalits from Tamil Nadu share more with each other than either do with Brahmins from their own regions (though again, Chamars share more with Brahmins from Uttar Pradesh than Dalits from Tamil Nadu, in part because of gene flow from Indo-Aryan steppe pastoralists into almost all non-Munda people in the Indo-Gangetic plain).
 When I read Castes of Mind: Colonialism and the Making of Modern India in the middle 2000s it seemed a persuasive enough argument to me. I had read other things about caste during that period, by both Indians and non-Indians. The authors were historians and anthropologists and emphasized the cultural and social preconditions variables shaping the emergence of caste..
When I read Castes of Mind: Colonialism and the Making of Modern India in the middle 2000s it seemed a persuasive enough argument to me. I had read other things about caste during that period, by both Indians and non-Indians. The authors were historians and anthropologists and emphasized the cultural and social preconditions variables shaping the emergence of caste..
The genetic material at that time did not have the power to detect fine-grained differences (classical autosomal markers) or were only at a single locus (Y, or, more often mtDNA). By the middle to late 2000s there was already suggestion from Y/mtDNA that there was some serious population structure in South Asia, but there wasn’t anything definitive.
 A full reading of works such as Castes of Mind leaves the impression that though some aspect of caste (broad varnas) are ancient, much of the elaboration and detail is recent, and probably due to British rationalization. The full title speaks to that reality.
A full reading of works such as Castes of Mind leaves the impression that though some aspect of caste (broad varnas) are ancient, much of the elaboration and detail is recent, and probably due to British rationalization. The full title speaks to that reality.
This is one reason I was surprised by the results from genome-wide analyses of Indian populations when they first came out. On the whole, populations at the top of the caste hierarchy were genetically distant from those at the bottom, and the broad pattern of the differences was mostly consistent across all of South Asia.
To give a concrete example, there are “lower caste” groups in Punjab which may have more steppe pastoralist ancestry than South Indian Brahmins. But within Punjab “highest caste” groups still have more ancestry than “lower caste” groups.
But this wasn’t the most shocking aspect. That was the fact that many castes are genetically quite distant, and anciently so. In a recent paper, The promise of disease gene discovery in South Asia:
We identify 81 unique groups, of which 14 have estimated census sizes of more than a million, that descend from founder events more extreme than those in Ashkenazi Jews and Finns, both of which have high rates of recessive disease due to founder events.
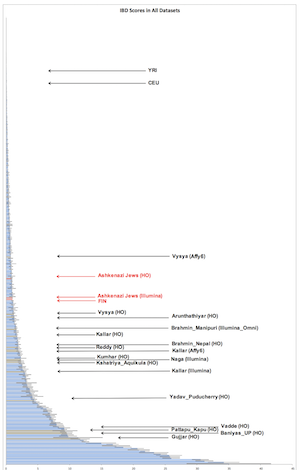 Some of this is due to consanguinity among Muslims and some South Indian groups, but much of it is not. Rather, it’s because genetically it looks like many Indian communities stopped intermarrying ~1,500 years ago. This reduces the effective number of ancestors even in a large population due to increased drift. At a recent conference, an Indian geneticist suggested that this might have something to do with the crystallization of caste Hinduism during the Gupta period. I can’t speak to that, but anyone who has looked at the data sees this pattern.
Some of this is due to consanguinity among Muslims and some South Indian groups, but much of it is not. Rather, it’s because genetically it looks like many Indian communities stopped intermarrying ~1,500 years ago. This reduces the effective number of ancestors even in a large population due to increased drift. At a recent conference, an Indian geneticist suggested that this might have something to do with the crystallization of caste Hinduism during the Gupta period. I can’t speak to that, but anyone who has looked at the data sees this pattern.
To illustrate what I’m talking about, assume ~1% introgression of genes from the surrounding population in a small group. Within 1,500 years 50% of the genes of the target population will have been “replaced.” The genetic patterns you see in many South Asian groups indicates far less than 1% genetic exchange per generation for over 1,000 years in these small groups.
But this post isn’t really about genetics. Rather, I began with the genetics because as an outsider in some sense I’ve never really grokked South Asian communalism on a deep level. Yet the genetics tells us that South Asians are extremely endogamous. It is unlikely that this would hold unless the groups were able to suppress individuality to a great extent. Though people tend to marry/mate with those “like them”, usually the frequency is not 99.99% per generation.
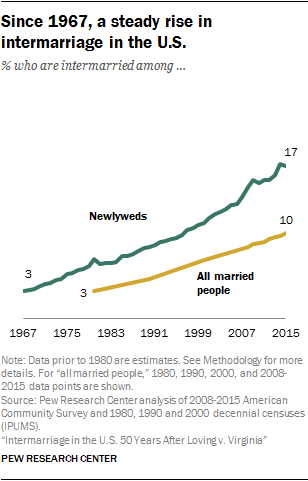 In the United States, things are different. Interracial marriage rates were ~1% in 1960.* This was still during the tail end of Jim Crow in much of the south. Since then the fraction of couples who are in ethno-racial mixed marriages keeps increasing and is almost 20% today. There is still a lot of assortative mating, and ingroup preference. But fractions in the 10-20% range are worrisome for anyone who is concerned about genetic cohesion over a few generations.
In the United States, things are different. Interracial marriage rates were ~1% in 1960.* This was still during the tail end of Jim Crow in much of the south. Since then the fraction of couples who are in ethno-racial mixed marriages keeps increasing and is almost 20% today. There is still a lot of assortative mating, and ingroup preference. But fractions in the 10-20% range are worrisome for anyone who is concerned about genetic cohesion over a few generations.
Though some level of group solidarity exists, explicitly among minorities, and implicitly for non-minorities, individual choice is in the catbird seat today. This was not always so. By the time I was growing up in the 1980s social norms had relaxed, but a black-white couple still warranted some attention and notice. In earlier periods interracial couples had to suffer through much more ostracism from their families and broader society.
In some South Asian contexts, this seems to be true to this day. But unlike the United States the situation is much more complex, with numerous ethno-religious-linguistic subgroups operating in a fractured landscape of power and identity.
I have wondered in part whether the South Asian fixation on sensitivity and feeling when it came to offense and insult is a function of the strong communal/collective aspect to honor, identity, and decision-making. Muslims outside of South Asia are similar to this, and in the Islamic context the rationale is quite explicit: non-Muslims and heretics are tolerated so long as they don’t challenge the public ethno-cultural supremacy of Islam. For example, atheism is punished less because of deviation from religious orthodoxy and more because it destabilizes public order and is seen as a crime against the state.
The conflicts between Hindus and Muslims in relation to religious parades have their clear analogs to strife between the dominant Catholics and the new Protestant communities in Latin America. But among Hindus the same tendencies crop up in inter-caste conflicts. The sexual brutalization that is sometimes reported of lower caste women by upper castes in parts of the Gangetic plain is a trivial consequence of the power that land-holding upper castes have over all the levers of power over low castes in certain localities. Lower caste men are powerless to defend their women against violation, just as in the American South enslaved black men couldn’t shield their womenfolk from the sexual advances of white men.
Will any of this change? I suspect that economic development and urbanization is the acid that will start to break down these old tendencies and relations in South Asia. It also seems clear that all South Asian communities which are transplanted to the more individualistic West have issues with the fact that collective and communal power is not given any public role, and in a de facto sense has to face the reality that individual choices in mates and cultural orientation are much more viable in the West.
This is particularly important to keep in mind on a blog like this, where many people are reading from South Asia (mostly India) and many are reading in the USA and UK. The conflict of values and signifiers occasionally plays out in these comments! For example, a Hindu nationalist commenter once referred to me as “Secular.” As an atheist, materialist, and someone who is irreligious in terms of identity and affiliation, secular describes me perfectly…in the West. But I was aware of the connotations of the term in India in particular, I told him that in fact, I wasn’t “Secular” in the way he was suggested. The reality is that unlike Indian Americans I don’t take a strong interest in what India does so long as it’s a reasonably stable regime, and so don’t signal my affiliation with Hindu nationalism or anti-Hindu nationalism.
* Latinos were not counted as part of this in 1960, so the rate looking at those numbers is 0.4%. I assume this is an underestimate because of Latinos.
Polyandry in Ceylon/Sri Lanka
Polyandry
There is an old Sinhala saying where four breasts cant get along, four heads can.
Many are under the impression that polyandry was some ancient/mythical social structure ( (e.g. Draupadi in the Mahabaratha).
To the the contrary it was prevalent till modern times in Sri Lanka/Ceylon, Nepal and certain groups in India. In Ceylon polyandry was prevalent till the 1950’s in the remote parts of the Kandyan kingdom, e.g. Nuwara-Kalaviya. Apparently there is a rise in fraternal polyandry in the Malwa region of the Punjab (see wiki on Polyandry).
The dynamics and customs of polyandry differ among the various cultures. I’ll only write about polyandry in Ceylon/Sri Lanka.
There were two types of unions, Deega amd Binna (those terms are still kind of used or understood). Diga was where the woman went to the man’s house. Binna was weh the man went to the woman’s house.
Deega: Where a woman went man/mens house. When she went to the men/mens house she was entitled to a share of the property that belonged to the house and income thereof. So if a woman had a union with 3 men she was entitled to 1/4th of the property and its income.
Knox, mentions that the dowry was considered the property of the wife and she was free to take it away, should the marriage be a failure. Among the things that were given as a part of the dowry Knox mentions slaves, cattle, tools and money. NOTE: Dowry was movable assets, not land.
Now at some point the woman gets tired of the men, or the men get tired of the woman. The woman will move back to her house (note I did not say parents house). When she moves back, her house property share has to be given back to her.
Binna: Thats when a man moves into the woman’s house. This could be a womans first unions or after she walks away from a Diga union and she is back in her house. They can get an income from either administering or working the woman’s share of the property.
Binna or Diga, the children remain in the house they were born and will inherit a share with other children also born in the house. The children dont belong to the parents, they belong to the house.
The Sinhalese names are based on the house. e.g. Galaha Lekamge Sunil. Written in English custom it would be Sunil of the Secretary’s house in Galaha (a village). The suffix “ge” pronounced “gay” means house or of.
Some key points that made the system work.
The house was an entity and had property (rice paddy, coconut groves etc). The property was not necessarily adjacent to the house.
Property could not be bought or sold.
Children belong to the house, not to either parent.
Minimum children: Infanticide and abortion were practiced. Infanticide was not gender based, but because the “horroscope” was bad.
Virginity for women and men was a non issue.
Knox (1681) says (1681):
- “In this country each man, even the greatest, hath but one wife; but a woman often has two husbands. For it is lawful and common with them for two brothers to keep house together with one wife, and the children do acknowledge and call both fathers”.
- These women are of a very strong and courageous spirit, taking nothing very much to heart, mourning more for fashion than affection, never overwhelmed neither with grief of live. And when their husbands are dead, all their care is where to get others, which they cannot long be without.”
- Their marriages are but of little force or validity for if they disagree and mislike one another, they part without disgrace…. Both women and men do commonly wed four or five times before they can settle themselves to their contention.”
- As soon as the child is born, the father or some friend apply themselves to an astrologer to inquire whether the child was born in a prosperous planet and a good hour or in an evil one. If it is found to be in an evil they presently destroy it.”
Links/refs
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polyandry_in_India
Robert Knox (1681) “An historical relation of the Island Ceylon in the East Indies”. Complete book is online
http://www.gutenberg.org/etext/14346
Knox was captured by the Kandyan King and was kept for 20 years. Escaped and wrote about life in the Hill Country. Supposed to have inspired Defoes, Robinson Crusoe
